What China's uneven recovery means for the U.S.
Add Axios as your preferred source to
see more of our stories on Google.
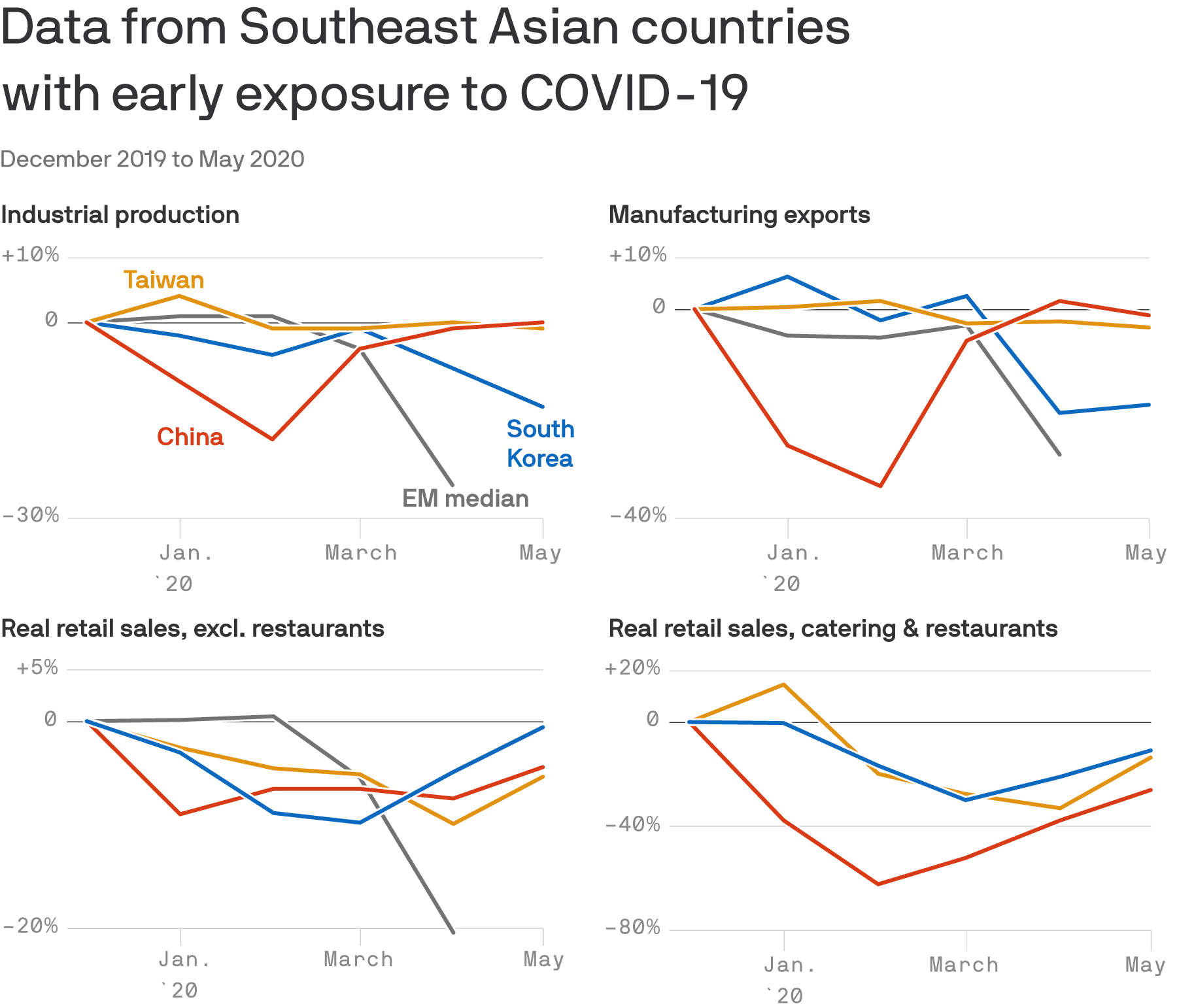
China and much of Southeast Asia look to be bouncing back strongly from the coronavirus pandemic as stock markets and much of the country's economic data are returning to pre-pandemic levels.
What's happening: "Our tracking points to a clear V-shaped recovery in China," economists at the Institute of International Finance said in a note to clients Tuesday, predicting the country's second-quarter growth will rise above 2% after its worst quarter on record in Q1.
- "The manufacturing recovery appears complete and exports also normalized."
By the numbers: Investors have responded by sending Chinese stocks skying — the CSI 300 index of Shanghai and Shenzhen-listed shares jumped as much as 5.7% on Monday, the biggest daily gain since February 2019 — thanks in no small part to urging from the Chinese Communist Party encouraging retail investors to buy stocks (subscription).
- And while U.S. shares retreated on Tuesday, the CSI 300 touched a new five-year high and rose again on Wednesday.
- The CSI 300 is up more than 15% in local currency terms year to date and over 18% since June 1.
Yes, but: While Chinese services sector data has rebounded, according to official and private sector data, IIF economists warn, "Consumption is still heavily disrupted. Retail sales are significantly below pre-COVID-19 levels and look U-shaped at best."
Why it matters: Many in the U.S. have looked to China as a model for an eventual U.S. rebound, but the details of China's recovery belie that hope.
- In addition to China's ability to contain its coronavirus outbreak much more quickly and effectively, manufacturing makes up nearly 30% of its economy, compared to around 10% for the U.S., according to the latest data from the World Bank.
- Services, driven by things like retail sales and restaurants, make up a little over half of China's GDP versus more than three-quarters of GDP for the United States.
Between the lines: China's manufacturing also has been heavily supported by government stimulus — IIF estimates fiscal stimulus could add up to 7% to 9% of GDP, or $1 trillion to $1.3 trillion — and the growth of medical supply sales as a result of the pandemic.
The big picture: The key to a U.S. economic rebound will be a sustained revival in services — but data show that even in countries that were hit early and quickly contained their outbreak, recovery has been slow and incomplete in that sector.
